Malaria remains a leading cause of illness and death among children in South Sudan and the country faces a malaria outbreak every year, worsened by factors such as flooding, poverty, and a fragile health system.
According to Médecins Sans Frontières (MSF), despite the predictable recurrence of malaria peaks, immunization coverage remains inadequate, contributing to overcrowded health facilities and an unbroken cycle of severe cases.
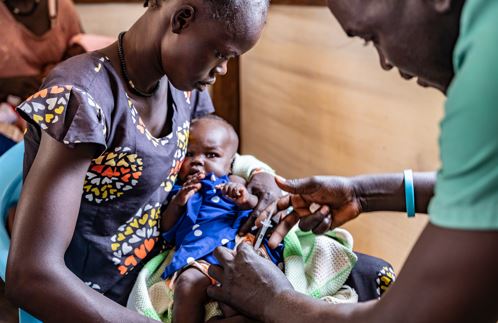
In response to these recurrent malaria outbreaks, MSF teams in Warrap State’s Twic County have implemented malaria prevention mass drug administration (MDA) and supported the Ministry of Health (MoH) in malaria vaccination rounds in Mayen Abun for the second year in a row. These preventive measures have contributed to a significant reduction in malaria cases and severity, especially among vulnerable children.
Adior Manut, from the Turalei internally displaced people’s camp in Mayen Abun in Twic County, said her children benefited from treatment by MSF and have not suffered from malaria.
“When the MDA started, I took my five children and got the drugs to prevent malaria. None of them got sick,” she said. “I appreciate that because I can’t imagine what my children would have been like if they hadn’t received this, how they could have suffered from malaria.”
Between May 2023 and October 2024, MSF launched seven rounds of the MDA campaign in Mayen Abun during malaria peaks to provide prophylaxis to children aged three months to 15 years. The target was to strengthen immunity and reduce cases among young children. By the end of October 2024, the team reached a total of 18,700 children with these MDA preventive measures.
Another mother, Arual Manyok, said there has been a big difference since the humanitarian medical charity introduced the Malaria Prevention Mass Drug Administration (MDA) in the area.
“If we compare before and after MSF started bringing malaria drugs, there is a big difference,” she stated. “All the children who received the drugs have never had malaria again. It is only the children who did not receive them who are getting sick.”
In July 2024, the South Sudanese authorities introduced the R21 malaria vaccine for existing malaria patients in high-burden areas such as Twic County, with MSF supporting the Ministry of Health (MoH) to roll out the vaccine for children aged five to 24 months.
As a result of preventive measures put in place, malaria cases in Twic have decreased.
“In our integrated case management community sites, for example, MSF recorded a decrease in malaria positivity rate consultation, from 79 percent between May to October in 2022, before MDA took place, to 70 percent in the same period in 2024,” an MSF statement said.
Dr. Mohamed Bashir, MSF project medical reference in Twic, affirms: “The decrease in malaria cases and severe admissions in 2024 clearly shows that malaria preventive measures like MDA prevention rounds or the malaria vaccine response by the MoH can effectively provide protection and interrupt the disease cycle in our target pediatric population.”
According to MSF, the effective results of their malaria prevention intervention were made possible by the active involvement of the community.
“MSF worked with health promotion teams, local volunteers, and leaders to raise awareness of malaria prevention and ensure that the most vulnerable children were protected,” the statement reads in part. “Despite the clear benefits of proactive prevention interventions in Twic County, lack of preparedness remains a concern in several regions of the country.”
MSF said recurrent malaria outbreaks continue to cause overcrowded health facilities and an increase in severe cases across South Sudan.
“Health organizations should invest in more robust prevention and emergency response. The success we have seen in Mayen Abun shows that malaria is preventable with the right tools,” Dr. Bashir said.