Health authorities in Tambura State say the region is still at risk of the Ebola outbreak saying new cases have been reported in neighboring Democratic Republic of (Congo DRC).
According to World Health Organisation, as of 7 October 2018, a total 181 cases had been confirmed, while 115 deaths reported from Congo’s nine health zones with the epicentre being Mabalako and Beni of North Kivu Province.
After a new outbreak last August, the South Sudan national health ministry and its partners launched wider Ebola sensitization campaigns in the former Western Equatoria State which share a common border with the Democratic Republic of Congo.
Tambura state Health Minister David Simbi told Radio Tamazuj on Wednesday that the border points with Congo remain closed except for those with screening centres to limit the risk of Ebola spreading into the region.
Simbi confirmed that no positive cases have been reported in Tambura so far but warns citizens to be vigilant of the deadly disease.
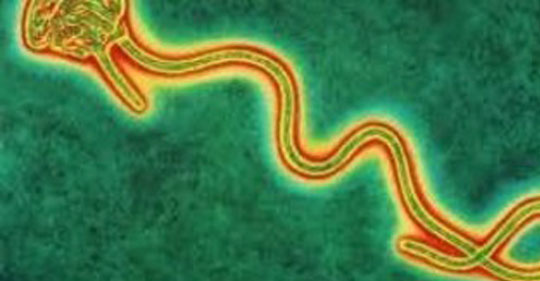
Ebola virus disease or Ebola hemorrhagic fever, is a fatal virus transmitted to people from wild animals and spreads in the human population through human-to-human transmission through direct contact with the blood, secretions, organs or other bodily fluids of infected people, and with surfaces and materials contaminated with these fluids.